Residential Proxies
Allowlisted 200M+ IPs from real ISP. Managed/obtained proxies via dashboard.

Proxies
Residential Proxies
Allowlisted 200M+ IPs from real ISP. Managed/obtained proxies via dashboard.
Residential (Socks5) Proxies
Over 200 million real IPs in 190+ locations,
Unlimited Residential Proxies
Use stable, fast, and furious 700K+ datacenter IPs worldwide.
Static Residential proxies
Long-lasting dedicated proxy, non-rotating residential proxy
Dedicated Datacenter Proxies
Use stable, fast, and furious 700K+ datacenter IPs worldwide.
Mobile Proxies
Dive into a 10M+ ethically-sourced mobile lP pool with 160+ locations and 700+ ASNs.

Web Unblocker
View content as a real user with the help of ABC proxy's dynamic fingerprinting technology.
Proxies
API
Proxy list is generated through an API link and applied to compatible programs after whitelist IP authorization
User+Pass Auth
Create credential freely and use rotating proxies on any device or software without allowlisting IP
Proxy Manager
Manage all proxies using APM interface

Proxies
Residential Proxies
Allowlisted 200M+ IPs from real ISP. Managed/obtained proxies via dashboard.
Starts from
$0.77/ GB
Residential (Socks5) Proxies
Over 200 million real IPs in 190+ locations,
Starts from
$0.045/ IP
Unlimited Residential Proxies
Use stable, fast, and furious 700K+ datacenter IPs worldwide.
Starts from
$79/ Day
Rotating ISP Proxies
ABCProxy's Rotating ISP Proxies guarantee long session time.
Starts from
$0.77/ GB
Static Residential proxies
Long-lasting dedicated proxy, non-rotating residential proxy
Starts from
$5/MONTH
Dedicated Datacenter Proxies
Use stable, fast, and furious 700K+ datacenter IPs worldwide.
Starts from
$4.5/MONTH
Mobile Proxies
Allowlisted 200M+ IPs from real ISP. Managed/obtained proxies via dashboard.
Starts from
$1.2/ GB
Knowledge Base
English
繁體中文
Русский
Indonesia
Português
Español
بالعربية
Title: Understanding IPv6: The Next Generation Internet Protocol
The Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) is the latest iteration of the Internet Protocol (IP) designed by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) to replace the aging IPv4 protocol. As the demand for unique IP addresses grows exponentially due to the proliferation of devices connected to the Internet, particularly in the era of the Internet of Things (IoT), IPv6 offers a solution by providing an immensely larger address space. This essay delves into the intricacies of IPv6, exploring its features, benefits, and significance in shaping the future of the Internet.
IPv4, the fourth version of the Internet Protocol, has been the backbone of the Internet since its inception in the 1980s. It uses 32-bit addresses, which theoretically allows for up to 4.3 billion unique addresses. However, with the explosion of devices connecting to the Internet, including smartphones, tablets, laptops, IoT devices, and more, IPv4's address space has become increasingly constrained. In 2011, the global pool of available IPv4 addresses was exhausted, leading to the urgent need for a successor protocol capable of handling the ever-growing demand for IP addresses.
Larger Address Space
IPv6's most significant feature is its vastly expanded address space. It employs 128-bit addresses, which translates to an astronomical number of unique addresses—approximately 340 undecillion (3.4 x 10^38) addresses. This immense address space ensures that every device, from smartphones to sensors in a smart city, can have its own unique IP address, eliminating the need for NAT (Network Address Translation) and other workarounds used in IPv4 networks to conserve addresses.
Improved Routing Efficiency
IPv6 introduces several routing improvements over IPv4. One notable feature is the hierarchical addressing structure, which allows for more efficient routing and aggregation of IP addresses. This hierarchical addressing not only simplifies network management but also improves the scalability of the Internet. Additionally, IPv6 uses larger routing tables, enabling routers to handle more entries and thus reducing the need for frequent updates.
Enhanced Security
IPv6 integrates IP Security (IPsec) protocols at the network layer, providing end-to-end security for data packets. This built-in security feature ensures that data transmitted over IPv6 networks is encrypted and authenticated, protecting against eavesdropping, tampering, and replay attacks. In contrast, IPv4 relies on higher-level protocols or application-specific security measures, which can be more vulnerable to attacks.
Better Support for Mobile Devices
IPv6 supports stateless address autoconfiguration (SLAAC), enabling devices to automatically configure their IP addresses when connecting to an IPv6 network. This feature is particularly useful for mobile devices, as it eliminates the need for manual configuration or DHCP servers, making it easier for devices to connect to the Internet and roam between networks.
Simplified Header Format
The IPv6 header is simpler and more efficient than the IPv4 header. It consists of only eight fixed-length fields, making packet processing faster and reducing the overhead associated with packet handling. In contrast, the IPv4 header can vary in size due to optional fields, making it more complex and less efficient.
Future-Proofing the Internet
With its vast address space, IPv6 ensures that the Internet can continue to grow and accommodate new devices and applications without facing the address exhaustion issues that plagued IPv4. This future-proofing is essential for the Internet's continued development and expansion.
Improved Security
The integration of IPsec in IPv6 provides a robust security framework for protecting data transmitted over the Internet. This enhanced security is vital for protecting sensitive information, such as financial transactions and personal data, from cyber threats.
Better Support for Emerging Technologies
IPv6's support for mobile devices, IoT, and cloud computing makes it an ideal choice for emerging technologies that rely on a vast network of interconnected devices. As these technologies continue to evolve, IPv6 will play a critical role in enabling their seamless integration and operation.
Improved Efficiency and Scalability
IPv6's simplified header format, hierarchical addressing structure, and larger routing tables contribute to improved network efficiency and scalability. These features make it easier for network administrators to manage large, complex networks and ensure that they can handle the increasing demand for bandwidth and connectivity.
IPv6 represents a significant step forward in the evolution of the Internet. Its vast address space, improved security, and support for emerging technologies make it an essential component of the future Internet. As the world becomes increasingly connected, the demand for unique IP addresses will continue to grow, making the transition to IPv6 a necessity. By embracing IPv6, we can ensure that the Internet remains a vibrant, dynamic, and secure platform for communication, innovation, and growth.
Featured Posts
Popular Products
Residential Proxies
Allowlisted 200M+ IPs from real ISP. Managed/obtained proxies via dashboard.
Residential (Socks5) Proxies
Over 200 million real IPs in 190+ locations,
Unlimited Residential Proxies
Use stable, fast, and furious 700K+ datacenter IPs worldwide.
Rotating ISP Proxies
ABCProxy's Rotating ISP Proxies guarantee long session time.
Residential (Socks5) Proxies
Long-lasting dedicated proxy, non-rotating residential proxy
Dedicated Datacenter Proxies
Use stable, fast, and furious 700K+ datacenter IPs worldwide.
Web Unblocker
View content as a real user with the help of ABC proxy's dynamic fingerprinting technology.
Related articles

2025 Easy-to-use Anti-detect Browser - BitBrowser
2025 Easy-to-use Anti-detect Browser - BitBrowser, ABCProxy

Unlock the Power of Genlogin with ABCproxy: A Game-Changing Combination
Looking for a reliable Genlogin service? ABCproxy has got you covered. Discover secure and seamless login solutions with Genlogin on ABCproxy for ultimate online protection. Safeguard your data with ease.
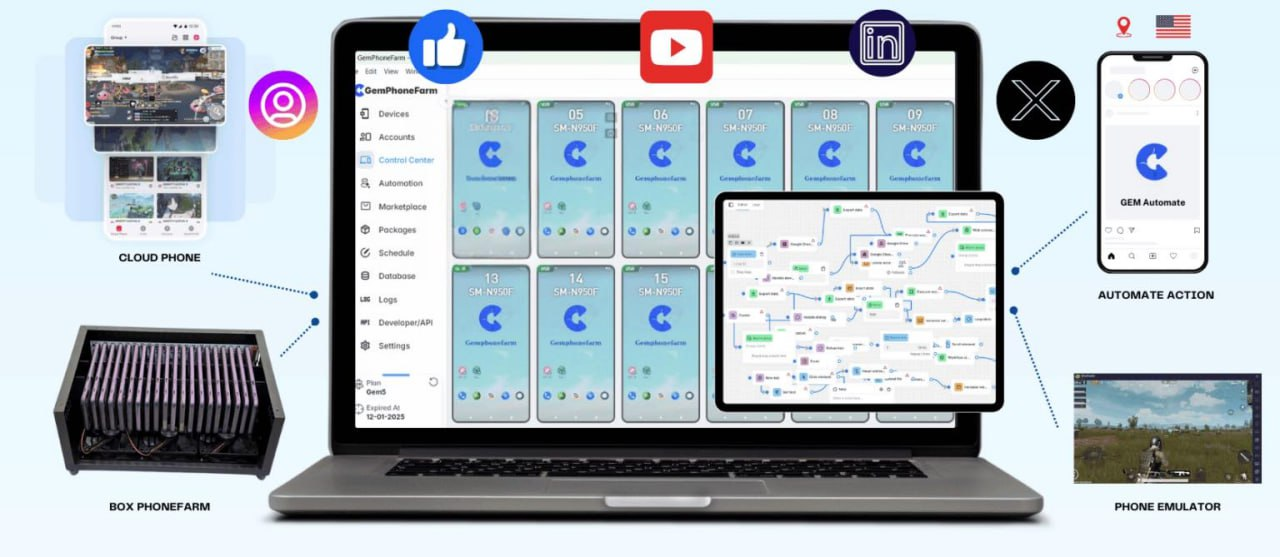
Unlock Untraceable Surfing: Gemlogin Antidetect Browser Boosted by ABC Proxy
Gemlogin Antidetect Browser With ABC Proxy provides advanced security features for online activities. Enjoy secure browsing with anonymity and protection. Safeguard your data with this powerful combination of features.